Can You Get a Car Back That Has Been Repossessed
Did you ever imagine that just one missed car payment could lead to your vehicle being repossessed? Unfortunately, it’s a reality many people face. Knowing the ins and outs of the repossession process can save you from the heartache of losing your car and the negative impact on your financial future. In this blog post, we will guide you through understanding car repossession, strategies for getting your car back, navigating your rights during the process, and answering the question, “can you get a car back that has been repossessed?” We will also discuss how to prevent future repossessions.
Short Summary
- Car repossession is typically caused by non-payment or lack of insurance and can be avoided if loan terms are adhered to.
- Strategies such as loan reinstatement, redemption, and bidding at auction may help recover a repossessed car depending on the financial situation.
- Borrowers have legal protections during the process that must be respected. Negative information resulting from repossession can remain on credit reports for up to seven years.
Understanding Car Repossession

Car repossession occurs when a borrower fails to make their car loan payments, resulting in the vehicle being reclaimed by the lender as collateral. Although the repossession process typically begins after two or three missed payments, it is possible for a car to be repossessed after just one missed payment. While repossession can have severe consequences on borrowers’ financial situation and credit report, understanding the process and the reasons behind it can help borrowers better navigate this tough situation and possibly prevent it from happening in the first place.
In the next sections, we will delve into the reasons for car repossession and the repossession process itself, providing valuable insights that can help you take control of your financial future.
Reasons for Car Repossession
The most common causes of car repossession are non-payment and absence of insurance. After repossession, the lender sells the car at an auction to recover the outstanding loan amount. The number of missed payments before car repossession is determined by the loan agreement, so it’s crucial to pay the entire loan balance or work out a payment plan with your lender to avoid repossession.
It’s essential to stay in touch with your lender and keep them informed about your situation. Lenders typically send notifications via telephone or post about the reasons for possible repossession, such as lack of insurance or failure to abide by the agreed terms of payment. In some cases, borrowers may opt for voluntary repossession to avoid additional fees and damage to their credit score.
The Repossession Process
After a car is repossessed, the auto lender is obligated to provide a written notification containing information about:
- The repossession
- The total amount owed on the car loan
- Late fees
- Towing costs
- Storage fees
- Other applicable repossession costs
The lender must also provide a timeline for the payment of the full amount if the borrower wishes to retain the car. The repossessed car is then transported to a storage facility and prepared for auction sales.
Repossession companies, also known as repo agents, follow state laws and the loan agreement when reclaiming a vehicle. They can enter a property and take a car from an unlocked driveway, but they must not commit any disturbances or breaches of the peace, such as breaking into a locked garage. It pays to know the ins and outs of the repossession process. This knowledge can help prevent potential issues with the repossession company.
Strategies to Recover Your Repossessed Car
If your car has been repossessed, don’t lose hope just yet. There are several strategies to get your car back after repossession, such as loan reinstatement, loan redemption, and bidding at auction. However, the availability of these options depends on your financial situation, the lender’s policies, and the state laws.
In the following subsections, we will discuss these strategies in detail, providing you with valuable information that can help you make an informed decision about getting your car back.
Loan Reinstatement
Loan reinstatement involves the following steps:
- Paying the past due payments and associated fees to regain possession of your vehicle.
- Satisfying any missed or overdue payments.
- Committing to sustaining future payments.
Generally, the payment for the loan reinstatement is due 10 to 20 days following the repossession of the vehicle.
Before considering loan reinstatement, it’s essential to evaluate whether you will be able to afford the car in the future, taking into account both car payments and associated expenses. If you decide to reinstate your loan, contact your lender without delay, as these transactions require prompt attention.
Loan Redemption
Loan redemption involves paying the full outstanding balance and requisite repossession fees to recover your car. In addition to paying the remaining loan balance, you’ll also need to cover repossession fees and storage fees. Before choosing loan redemption as a strategy to reclaim your car, you should consider whether you can afford the costs of insuring and maintaining the car.
If you’re unable to pay the full outstanding balance in a lump sum, you may still have other options, such as reinstating your loan or bidding on your car at the lender’s auction, as discussed in the previous and following subsections.
Bidding at Auction
Attending the lender’s auction to bid on and potentially buy back the repossessed car is another option you can consider. In this case, you’ll need to settle the deficit balance and assume responsibility for the expenses of the public sale. Keep in mind that there’s a risk of another bidder offering a higher price and securing the car.
If you’re unable to reinstate or redeem your loan, participating in the auction might be your last chance to get your car back. However, make sure to weigh the costs and risks associated with bidding at the lender’s auction before making a decision.
Navigating Your Rights During Repossession
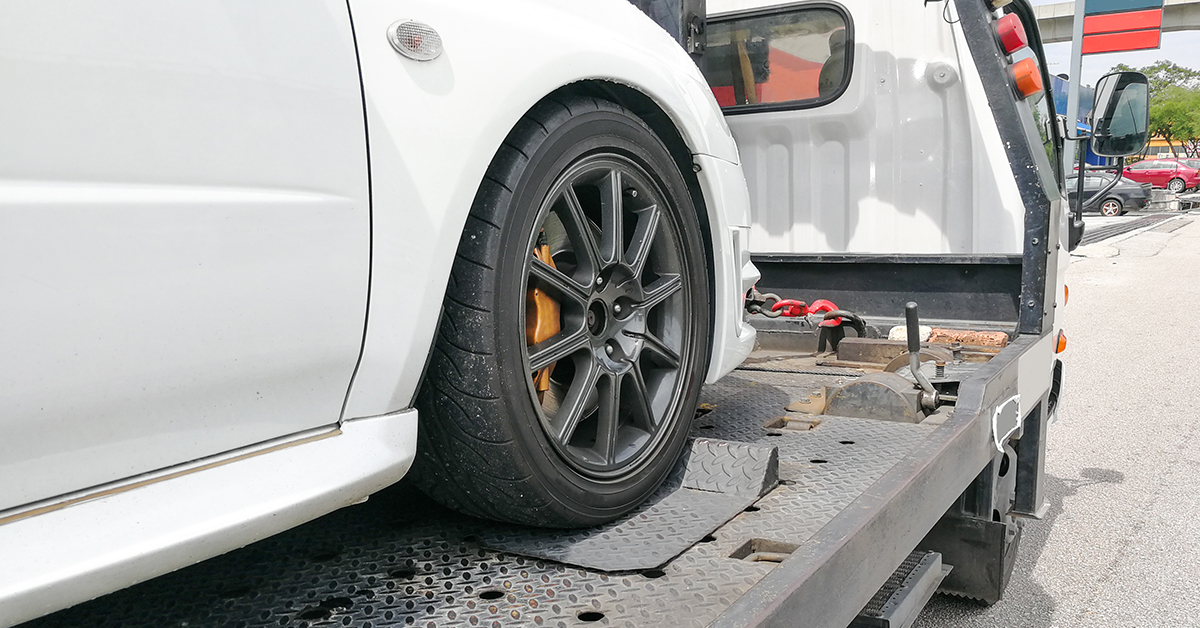

As a borrower, it’s crucial to know your rights and protections during the repossession process. Understanding your rights can help you ensure that the lender and repo agent act in accordance with the law and treat your case fairly.
In the next subsections, we will discuss borrower protections and the process of retrieving personal property from a repossessed car, providing valuable insights to help you navigate your rights during repossession.
Borrower Protections
Borrowers possess certain legal rights and protections during repossession. If you believe that your rights have been infringed upon during repossession, it’s recommended that you contact a lawyer who is familiar with the laws of your state to ensure that your rights are being respected.
Lenders are not permitted to take personal items left in the car during repossession or damage personal property. Stay informed about your rights and protections to avoid any potential complications with the lender or repossession company.
Retrieving Personal Property
To reclaim personal property during repossession, you should:
- Contact the creditor promptly.
- Note that the lender or repo agent typically cannot impose a fee to reclaim personal property, but the procedure may differ depending on the jurisdiction.
- The creditor must take reasonable steps to ensure that your personal property is not stolen or damaged, so you should be able to retrieve your items.
To guarantee the appropriate handling of your personal property, follow these steps:
- Communicate with the creditor promptly.
- Provide proof of ownership of the property.
- The creditor should then arrange for you to retrieve your personal property in a secure and safe manner.
Financial Considerations and Credit Impact

Car repossession can have significant financial consequences and affect your credit report. A repossession may remain on your credit reports for up to seven years, impacting your credit score and future borrowing opportunities.
In the following subsections, we will discuss deficit balances and surpluses, as well as the consequences of car repossession on your credit report, providing valuable information that can help you better understand the financial impact of repossession.
Deficiency Balances and Surpluses
A deficit balance is the amount of money that remains unpaid on a car loan after the car has been repossessed and sold at auction. If the proceeds from the sale are insufficient to cover the amount owed to the lender, you may be required to pay the remaining balance, referred to as a deficiency balance. If the deficiency balance is not paid, the account may be sent to collections, and the lender may initiate legal action to recover the amount.
On the other hand, if the lender sells your car for a higher amount than that of your loan and other expenses associated with repossession, you are eligible to claim the difference. This difference is known as a surplus.
Credit Report Consequences
Repossession will be reflected on your credit report from the three major credit bureaus and may remain there for up to seven years. This negative information can have a substantial impact on your credit score and your ability to secure future credit.
If you reach an agreement with your lender and start making new payments, your new payment history is likely to be reflected on your credit report. It’s essential to take measures to improve your credit score and prevent future repossessions, which could lead to even more severe financial consequences.
Preventing Future Repossessions
The best way to prevent future car repossessions is to learn from your past experiences and take proactive measures to ensure that you can afford the car and comply with the terms of your loan. Here are some steps you can take.
- Maintain open communication with your lender.
- Adhere to insurance and loan terms.
- Create a budget and stick to it.
- Save an emergency fund to cover unexpected expenses.
- Regularly review your financial situation and make adjustments as needed.
By following these steps, you can avoid the stress and financial impact of repossession.
In the following subsections, we will discuss the importance of open communication with lenders and the significance of maintaining insurance and loan terms, providing valuable tips that can help you prevent future car repossessions.
Open Communication with Lenders
Open communication with lenders is of great importance, as it facilitates the establishment of a strong rapport between you and your lender, helps them understand your financial situation, and aids in negotiating payment plans. Effective communication can lead to the lender offering alternative solutions and payment plans that can help you avoid repossession.
To facilitate effective communication with your lender, be honest and transparent about your financial situation, be proactive in communicating with them, and be open to negotiation.
Maintaining Insurance and Loan Terms
Complying with insurance and loan terms is essential to safeguard yourself from financial harm in the event of accidents or damage to your car and to prevent falling behind on your loan and losing your vehicle. Lenders require borrowers to maintain comprehensive coverage on their vehicles to protect their financial interests in the car.
To uphold your insurance and auto loan terms, ensure that your monthly payments are made timely and that your insurance coverage is kept current. Read and understand the terms of your loan agreement, and contact your lender if you have any questions or concerns.
Summary
In summary, understanding the repossession process, your rights, and the financial implications of car repossession is crucial for navigating this challenging situation. By employing strategies such as loan reinstatement, redemption, or bidding at auction, you may be able to recover your repossessed car. Maintaining open communication with your lender and adhering to insurance and loan terms can help prevent future repossessions. Knowledge is power, and by educating yourself on the ins and outs of car repossession, you can take control of your financial future and avoid the heartache of losing your vehicle.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does a repo stay on your credit?
A repossession stays on your credit report for seven years, starting from the date of the first missed payment that led to the repossession. During this time, you can still work to strengthen your credit by paying off existing debt and avoiding taking on more debt.
How do I remove a paid repossession from my credit report?
The only way to remove a paid repossession from your credit report is to negotiate with your lender and pay the debt in full. This will be the only option, aside from waiting seven years, that can potentially get the item removed from your credit report.
What are the repossession laws in New York City?
Car repossession laws are primarily regulated at the state level, so the rules that apply in New York City would be those of New York State. Here are some basic aspects of car repossession laws in New York State as of my last training cut-off in September 2021:
- Right to Repossess: If a borrower defaults on their auto loan, the lender has the right to repossess the vehicle. “Default” typically means failing to make timely payments, but the specific definition of default can vary depending on the terms of the loan agreement.
- No “Breach of the Peace”: Repossession agents must not “breach the peace” when taking a car. This means they cannot use physical force, threaten force, or remove a car from a closed garage without permission. If a breach of the peace occurs, the borrower may have grounds for a lawsuit.
- Notice After Repossession: After the vehicle has been repossessed, the lender is required to send the borrower a “Notice of Right to Reclaim the Vehicle.” This notice provides details on how the borrower can get the vehicle back, which usually involves paying back the loan in full plus any repossession and storage costs.
- Opportunity to Redeem: The borrower usually has a right to redeem (or buy back) the vehicle after repossession. This would involve paying off the entire loan balance, plus any fees or costs associated with the repossession.
- Reselling the Vehicle: If the borrower does not redeem the vehicle, the lender will typically sell the car, either through a private sale or public auction. New York law requires that the sale be conducted in a “commercially reasonable manner.”
- Deficiency Balances: If the vehicle is sold for less than the amount owed on the loan, the borrower is generally responsible for the difference, called a “deficiency balance.” Conversely, if the car sells for more than the loan balance, the lender must return the surplus to the borrower.
- License of Repossession Agents: In some states, repossession agents must be licensed. It’s always a good idea to check current state regulations to see if this applies in New York.
- Reinstating the Loan: Some states provide the right for borrowers to reinstate the loan after repossession by paying the past-due amount and any associated fees. Borrowers would then continue with the original loan terms. This isn’t a universal right, so one would need to check either the loan agreement or current New York regulations.
- Electronic Disabling Devices: Some vehicles come equipped with devices that can disable the car if the borrower misses payments. New York has specific laws regarding the use of these devices, ensuring that borrowers receive proper warning before the vehicle is disabled.
- Personal Property: If there are personal items in the vehicle at the time of repossession, the repossession agent must provide the borrower with an opportunity to retrieve those items. They can’t sell or keep personal belongings that were inside the vehicle.
If you’re facing a potential repossession, or if you’re a lender or repossession agent trying to understand your rights and responsibilities, it’s crucial to consult with a local attorney familiar with the most current New York State laws on the topic. Laws and regulations can change, and local attorneys will have the most up-to-date and relevant information.
What is the difference between loan reinstatement and redemption?
Loan reinstatement involves catching up on payments and fees, while loan redemption requires paying the full balance plus repossession fees to get your car back.
Can I bid on my repossessed car at the lender’s auction?
Yes, you can bid on your repossessed car at the lender’s auction.



 Who We Are
Who We Are Coverage Area
Coverage Area Donate
Donate