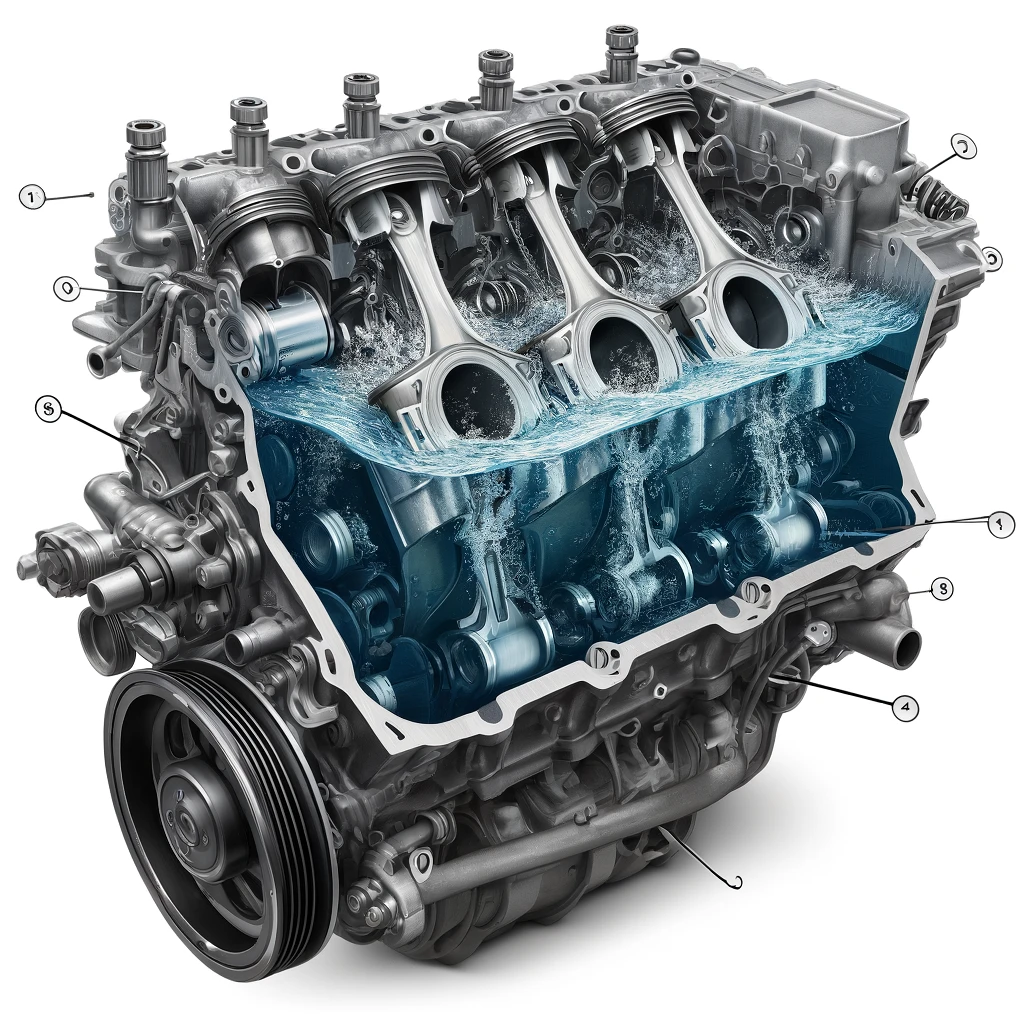

What is a Hydrolocked Engine?
Introduction
Understanding the concept of a hydrolocked engine is crucial for individuals at all levels of automotive expertise, from seasoned car owners to beginners just learning the ropes of vehicle maintenance. Hydrolocking, which is a severe and potentially catastrophic condition that can affect an engine, occurs when a significant amount of liquid, most commonly water, manages to infiltrate the cylinders of the engine. This detailed guide aims to provide you with a comprehensive overview of hydrolocking: delving into the causes behind this detrimental issue, outlining the telltale symptoms that indicate your engine might be hydrolocked, elucidating the ways in which hydrolocking can inflict substantial damage on your engine’s internal components, and presenting effective strategies and preventive measures to either steer clear of or effectively troubleshoot a hydrolocked engine should you encounter this alarming situation.
Hydrolocking of an engine can be instigated by a variety of circumstances, with the most prevalent cause being the unintentional ingestion of water through the engine’s air intake system. This can occur when driving through deep puddles, flooded roads, or even during off-road excursions where water crossings are involved. If the air intake system is placed in a low position within the vehicle, or if there are leaks or openings in the system, it becomes susceptible to drawing in water when submerged, leading to the potential hydrolocking of the engine.
Aside from the causes, recognizing the symptoms associated with a hydrolocked engine is pivotal in addressing the issue promptly and preventing further damage. Some common indicators that your engine may be hydrolocked include the engine refusing to turn over when attempting to start the vehicle, an unusual sound emanating from the engine bay during start-up, or visible signs of water exiting the exhaust pipe when the engine is cranked. Ignoring these warning signs and continuing attempts to start the engine can exacerbate the damage, potentially resulting in bent or broken internal engine components due to the incompressible nature of water when trapped within the cylinders.
Consequently, the aftermath of a hydrolocked engine can be financially burdensome, necessitating costly repairs or even engine replacement depending on the extent of the damage incurred. The force exerted by the incompressible nature of water entering the cylinders can cause severe mechanical stress on critical engine components, such as connecting rods, pistons, and valves, leading to deformation or fracture. In such cases, seeking professional assistance from a qualified mechanic is often imperative to assess the extent of the damage and determine the most appropriate course of action to rectify the situation.
What Causes a Hydrolocked Engine?
Entry of Water into the Engine
- Driving Through Flooded Areas: The most common cause of hydrolocking is when a vehicle drives through high water, allowing water to enter the intake system.
When water enters the engine, it can lead to a phenomenon known as hydrolocking, which can cause significant damage to the vehicle’s internal components. One common scenario in which water ingress occurs is when a vehicle traverses flooded areas. Driving through high water levels can allow water to penetrate the intake system, setting the stage for hydrolocking. Another potential cause is a faulty head gasket. If the head gasket is compromised, water from the cooling system might seep into the cylinders, increasing the risk of hydrolocking.
- Faulty Head Gasket: Water from the cooling system can leak into the cylinders due to a blown head gasket.
Additionally, improper car washing techniques can sometimes contribute to water entering the engine. When high-pressure water is directed near air intake areas during car washing, there is a possibility of water infiltrating the intake system, potentially leading to hydrolocking. Apart from water, other fluids such as engine coolant or oil can also pose a risk of hydrolocking if they leak into the combustion chamber. Engine fluid leaks are a concern as they can introduce non-compressible liquids into the cylinders, impeding the normal functioning of the engine and potentially causing hydrolocking issues.
- Improper Car Washing Techniques: High-pressure water can sometimes enter the intake if direct water pressure is applied near air intake areas.
Entry of Other Fluids
- Engine Fluid Leaks: Other engine fluids like coolant or oil can also lead to hydrolocking if they leak into the combustion chamber.
How Does Hydrolocking Occur?
- Engine Operation Basics: Briefly explain how a typical internal combustion engine works.
Hydrolocking occurs when a liquid enters the combustion chamber of an internal combustion engine, causing potentially severe damage to the engine components. To better understand how hydrolocking happens, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental operation of a typical internal combustion engine. In a nutshell, an internal combustion engine works by mixing fuel and air in a combustion chamber, where the mixture is ignited to produce the energy needed to power the vehicle. Unlike air, liquids are incompressible.
- When Liquid Enters: Unlike air, liquids are incompressible. When an engine’s piston attempts to compress liquid in the combustion chamber, it can lead to immediate engine stall, and in severe cases, it can cause mechanical damage, such as bent piston rods, cracked engine blocks, and damaged valves.
Therefore, when a liquid, instead of air, enters the combustion chamber, the piston’s attempt to compress this liquid can result in immediate engine stall. In more severe cases, hydrolocking can lead to significant mechanical damage, such as bent piston rods, cracked engine blocks, and damaged valves. The inability of the engine to compress the liquid effectively disrupts the normal cycle of operation, causing detrimental effects on the engine’s internal components. Consequently, understanding the risks and causes of hydrolocking is crucial in maintaining the health and performance of an internal combustion engine.
Symptoms of a Hydrolocked Engine

- Sudden Engine Stalling: The engine may abruptly stop if it becomes hydrolocked while operating.
Sudden engine stalling can occur when the internal combustion engine is hydrolocked during operation, leading to an abrupt halt in engine functioning. This phenomenon arises when the engine’s cylinders become flooded with non-compressible fluid, causing a significant disruption in the combustion process and resulting in the immediate cessation of engine operation.
- No Start with a Strange Sound: Attempting to start a hydrolocked engine might produce a distinct sound due to the hydraulic resistance.
When attempting to start a hydrolocked engine, a distinctive and unusual sound may be emitted, indicative of the hydraulic resistance impeding the normal ignition process. This distinct sound often serves as an auditory red flag, signaling the presence of hydraulic lock within the engine and the potential challenges that may arise from attempting to initiate the engine in such a compromised state.
- Visible Water in the Intake or Spark Plugs: Presence of water during spark plug or air filter inspection.
A clear indication of water intrusion into the engine system can be observed during routine spark plug or air filter inspections, where the presence of water within the intake components or on the spark plugs becomes visibly apparent. The detection of water in these critical engine areas serves as a visible manifestation of the potential hydrolocking threat, highlighting the need for immediate attention and remedial action to prevent further damage and restore optimal engine functionality.
Diagnosing a Hydrolocked Engine
- Visual Inspection: Checking for water in the intake manifold or the air filter. When diagnosing a hydrolocked engine, the first step is to conduct a visual inspection to check for any presence of water in the intake manifold or the air filter. However, for a more comprehensive diagnosis, it is advisable to seek professional help. A trained mechanic can perform a thorough evaluation, which may include conducting compression tests and checking the integrity of various engine components.
- Removing Spark Plugs: Spark plugs can be removed to see if water ejects from the combustion chamber when the engine is turned over manually. Additionally, removing the spark plugs is crucial in determining if water ejects from the combustion chamber when the engine is manually turned over. This visual inspection and spark plug removal are essential initial steps in identifying a hydrolocked engine.
- Professional Diagnosis: A mechanic can perform more detailed diagnostics, including compression tests and checking the integrity of engine components. These detailed diagnostics carried out by a professional can provide a more accurate assessment of the extent of water damage within the engine and help in devising an appropriate course of action to rectify the issue.
Repairing a Hydrolocked Engine
Immediate Actions
- Do Not Attempt to Start the Engine: This can cause more damage. Tow the car to a professional service if hydrolocking is suspected. When faced with a hydrolocked engine, it is crucial to handle the situation promptly and effectively. One of the immediate actions to take if you suspect a hydrolocked engine is to avoid attempting to start the engine. Doing so can lead to further damage to the vehicle. Instead, it is advisable to have the car towed to a professional service for a thorough inspection and repair. By refraining from trying to start the engine, you can prevent exacerbating the issue and increase the likelihood of successful restoration. This precautionary measure can ultimately save you time, money, and the hassle of dealing with more extensive engine damage. Taking swift and appropriate action in such a scenario is key to mitigating the effects of hydrolocking and ensuring the longevity of your vehicle’s engine.
Professional Repair
- Draining the Engine: Involves removing water from the combustion chamber.
- Checking for Damage: Inspecting and replacing damaged internal components.
- Engine Rebuild or Replacement: In cases of significant damage, a complete engine rebuild or replacement may be necessary.
Prevention Tips

- Avoid Driving Through Floods: Always take alternative routes if possible.
When it comes to professional repair of a water-damaged engine, the process typically involves several critical steps to ensure the engine’s optimal functionality is restored. The initial step in the repair process is draining the engine, which entails removing any water present within the combustion chamber to prevent potential damage to internal components.
- Regular Maintenance: Check and maintain engine fluids and seals regularly.
Following this, a thorough inspection is conducted to check for any signs of damage resulting from the water exposure. Damaged internal parts are identified and replaced as needed to guarantee the engine’s performance and longevity.
- Proper Car Washing Techniques: Be mindful of the car’s air intake placement when using high-pressure water.
In cases where the damage is extensive and cannot be adequately repaired through component replacement, the repair may necessitate a complete engine rebuild or replacement to ensure the engine’s proper functioning and longevity. This comprehensive approach to professional engine repair ensures that all potential issues are addressed, ultimately restoring the engine to its optimal working condition.
Conclusion
A hydrolocked engine is a serious issue that can lead to significant engine damage. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and preventive measures can help drivers maintain their vehicle’s health and avoid the costly and inconvenient consequences of engine hydrolocking.
FAQs
- Can a hydrolocked engine be fixed?
- How much does it cost to repair a hydrolocked engine?
- Can hydrolocking be covered by insurance?
Understanding the peril of a hydrolocked engine is crucial for all car owners. The term “hydrolock” describes a condition where a liquid, usually water, enters the engine’s cylinders, leading to potential catastrophic outcomes. This detailed exploration provides insights into the causes, detection, and resolution of hydrolocking, equipping drivers with the knowledge to prevent this disastrous scenario.
For more information, visit https://www.carmula.com/



 Who We Are
Who We Are Coverage Area
Coverage Area Donate
Donate