Have you ever wondered, “how heavy is a car in pounds or kilograms?” and why it’s essential to know? Car weight plays a vital role in performance, fuel economy, and safety. In this blog post, we will dive into the fascinating world of car weight, explore the factors influencing vehicle weight, and discuss the impact of weight on performance and efficiency. So, buckle up and get ready for an enlightening journey through the world of “how heavy is a car in kg!”
Key Takeaways
- Understanding car weight in pounds is important for fuel economy, performance and safety.
- Common car weights range from 2,500 to 6,000 lbs depending on body style and size.
- Manufacturers are striving to reduce vehicle weight for improved performance, efficiency & safety. It can be determined by using a VIN lookup or referencing owner’s manual/manufacturer website.
Understanding Car Weight in Pounds

Car weight in pounds refers to the total weight of a vehicle, including passengers, cargo, and any optional or extra equipment. It is usually determined by the “curb weight” metric, which is the weight of the vehicle with standard equipment and a full tank of fuel, excluding optional equipment, passengers, or any other extras.
The average weight of a car is approximately 4,329 pounds, while a full-size car typically weighs roughly 3,800 pounds. The weight of trucks and SUVs can range from approximately 3,500 pounds to over 6,000 pounds. Grasping the concept of car weight is vital because it directly affects fuel economy, performance, and safety.
From Pounds to Kilograms
While car weight is often discussed in pounds, especially in the United States, it is essential to convert these figures to kilograms for international understanding. One pound is approximately equal to 0.45359237 kilograms (kg). To convert car weight from pounds to kilograms, simply divide the weight in pounds by 2.2046.
Converting car weight to kilograms is important since it ensures global consistency and simplicity in discussions about car weights, including gross combined weight.
Common Car Weight Ranges
Car weight varies based on body style and size, and understanding how much a car weighs can be useful for various purposes. Here are some general weight ranges:
- Compact cars: 2,500 to 3,000 pounds
- Sedans: 3,000 to 4,000 pounds
- SUVs: 4,000 to 5,000 pounds
- Trucks: 4,000 to 6,000 pounds
- Sports cars: 2,500 to 3,500 pounds
Familiarizing yourself with these weight ranges can enhance your understanding of your vehicle’s weight and how it influences performance, fuel efficiency, and safety.
Factors Influencing Vehicle Weight
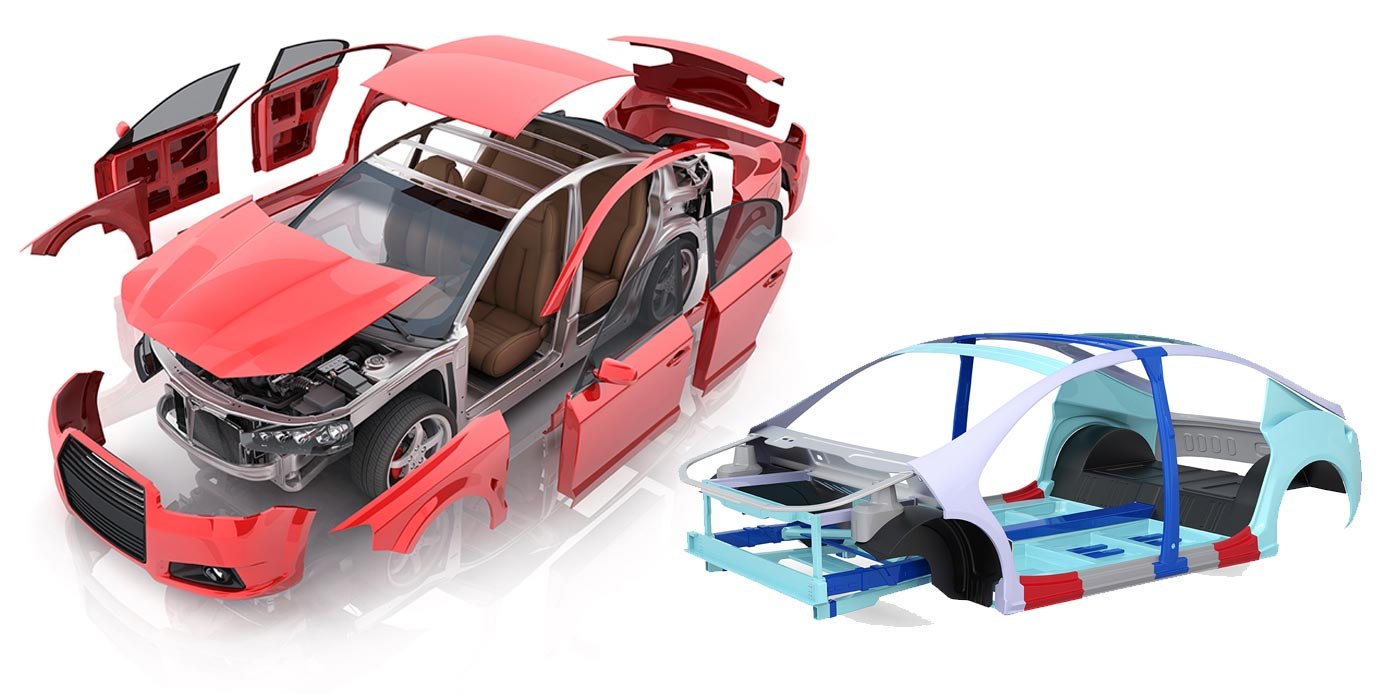
Several factors influence vehicle weight, such as materials and construction, safety features and technology, and the use of electric vehicles and batteries. The weight of a car can have a direct impact on its performance, fuel efficiency, and safety. Heavier vehicles tend to consume more fuel, have slower acceleration, and require more force to stop.
Conversely, lighter vehicles generally offer better fuel economy and maneuverability. Comprehending these factors can assist you in making well-informed decisions about vehicle purchases, maintenance, and operation.
Materials and Construction
Materials and construction methods play a significant role in determining a car’s weight. Common materials used in automobile construction include:
- Steel
- Rubber
- Plastics
- Aluminum
The use of steel, particularly Advanced High-Strength Steels (AHSS), can reduce the structural weight of a vehicle by up to 25 percent and total vehicle weight by 8-10 percent compared to other materials.
Aluminum is another lightweight material that can make a vehicle up to 45 percent lighter, resulting in enhanced fuel economy and increased range in electric vehicles. Carbon fiber is also used in car construction due to its lightweight properties and high weight reduction potential.
Safety Features and Technology
Safety features and technology have a substantial impact on car weight. Recent safety regulations necessitate the inclusion of features such as airbags, door intrusion beams, and tire-pressure monitors, which add weight to vehicles. Additionally, luxury amenities like real-time navigation systems, seat cooling and heating systems, and entertainment systems contribute to increased vehicle weight.
However, manufacturers are continuously working on developing lighter safety components and materials to balance between safety and fuel efficiency.
Electric Vehicles and Batteries
Electric vehicles (EVs) and their batteries also influence car weight. EV batteries can be significantly heavier than traditional internal combustion engines. For instance, the 2023 GMC Hummer EV weighs over 9,000 pounds, with a 2,900-pound battery. The materials used in EV batteries, such as:
- lithium
- cobalt
- manganese
- graphite
- steel
- nickel
Factors that contribute to their maximum weight.
However, the positioning of the battery in an EV can impact the overall weight distribution, affecting the vehicle’s handling and performance.
Average Car Weights by Body Style

Having examined the factors that influence car weight, we can now consider the average car weights by body style. Here are the average car weights for each body style:
- Compact cars: around 2,600 pounds
- Midsize cars: approximately 3,300 pounds
- Subcompact SUVs: around 3,250 pounds
- Larger SUVs (e.g. Chevy Suburban): up to 5,700 pounds or more
Trucks also vary in vehicle weights, with light-duty trucks weighing between 4,000 to 7,000 pounds. Sports cars have an average weight of around 3,100 pounds, as reported by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
Compact Cars
Compact cars are known for their fuel efficiency and maneuverability, partly due to their lighter weight. The weight of a compact car is usually quite low. On average, it weighs around 2,600 pounds. Popular compact car models and their respective weights include the Toyota Corolla at 2,955 pounds, the Tesla Model 3 at 3,648 pounds, and the Honda Civic, which ranges from 2,935 to 3,077 pounds depending on the trim level.
Sedans
Sedans are a popular choice for families and individuals alike, offering comfort and practicality. The average weight of a sedan is approximately 3,351 pounds or 1,520 kilograms.
Some popular sedan models and their respective weights include the Toyota Camry, weighing between 3,310 and 3,475 pounds depending on the trim and drivetrain, the Nissan Altima, with a weight range of 3,244 to 3,460 pounds, and the Subaru Legacy, weighing between 3,491 and 3,787 pounds.
SUVs
SUVs are favored for their versatility, spaciousness, and off-road capabilities. The weight of SUVs can vary greatly depending on their size. Subcompact SUVs, such as the Mazda CX-5, Chevrolet Equinox, and Toyota Rav4, have weights ranging from around 3,100 to 3,800 pounds.
On the other hand, full-size SUVs like the Chevrolet Suburban and Ford Expedition can weigh up to 5,700 pounds or more.
Trucks
Trucks are known for their towing and payload capabilities, making them ideal for heavy-duty work and off-road adventures. The average weight of a pickup truck ranges from 4,000 to 7,000 pounds.
Popular truck models and their respective weights include the Ford F150, weighing between 4,069 and 5,517 pounds depending on the configuration, and the Toyota Tundra, with a weight range of 4,920 to 5,670 pounds.
Sports Cars

Sports cars are designed for performance and speed, usually featuring powerful engines and lightweight materials. The average weight of a sports car is approximately 3,100 pounds, as reported by the EPA. Some popular sports car models and their respective weights include the Mazda Miata at 2,341 pounds, the Porsche Cayman, with a weight range of 3,040 to 3,227 pounds, and the Audi R8, weighing 3,571 pounds.
The Impact of Car Weight on Performance and Efficiency
Car weight significantly influences performance, fuel efficiency, and safety. Heavier vehicles typically exhibit slower acceleration, need more force to stop, and use more fuel. In contrast, lighter vehicles tend to provide better fuel economy and maneuverability.
In recent years, manufacturers have been working to develop lighter safety components and materials to balance between safety and fuel efficiency without compromising performance.
Performance
A car’s weight significantly influences its performance characteristics, such as acceleration, handling, and braking. Heavier cars need more energy to accelerate and alter direction, resulting in slower acceleration and handling. Moreover, due to their increased inertia and slower direction change rate, heavier cars require longer distances to brake.
Weight distribution also plays a crucial role in a car’s performance, with a balanced distribution allowing for better handling and braking.
Fuel Efficiency
The weight of a car directly influences its fuel efficiency. Heavier vehicles, due to their greater inertia and rolling resistance, burn more fuel. On the flip side, lighter cars need less fuel to move, thus improving their fuel economy.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has reported that for every 100 pounds removed from a vehicle, fuel economy can be increased by 1-2 percent. This highlights the importance of minimizing car weight for better fuel efficiency.
Safety
Vehicle safety is heavily influenced by car weight. Heavier, larger vehicles generally provide better protection in multi-vehicle crashes than smaller, lighter cars. Nonetheless, lighter cars built with sturdy materials have been associated with a decrease in fatalities per vehicle miles traveled.
Safety technologies such as automatic brake assist and electronic stability controls can also help enhance the safety of lighter vehicles. Ultimately, understanding car weight is vital for making informed decisions about vehicle safety.
How to Determine Your Car’s Weight
If you’re curious about the weight of your car, there are several methods to help you determine it. You can use a Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) lookup, refer to your car’s owner’s manual, or visit the manufacturer’s website for specific weight information.
Being aware of your car’s weight is essential for making well-informed decisions about vehicle purchases, maintenance, and operation.
Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) Lookup
A vehicle identification number (VIN) lookup is a useful tool for determining your car’s weight. The VIN is a unique identifier for your vehicle and can be found on the driver’s side dashboard or door jamb. A VIN lookup service uses the VIN to retrieve information about your vehicle, such as its make, model, and weight.
Many dependable online platforms offer VIN lookup services, such as ClearVIN, National Insurance Crime Bureau (NICB), and VehicleHistory.com.
Owner’s Manual
Your car’s owner’s manual is another valuable resource for determining its weight. The manual typically contains information regarding the vehicle’s curb weight, gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR), gross axle weight rating, and gross combination weight rating. Additionally, it may provide details about the gross vehicle weight gvw. You can find this information in the specifications or technical information section of the manual.
In addition to car weight, the owner’s manual may also provide guidance on proper vehicle maintenance and safety precautions.
Manufacturer’s Website
Finally, the manufacturer’s website can provide specific car weight information. By navigating to the website and searching for your car’s model, you can find weight details in the specifications or technical information section. The website may provide information on the car’s curb weight, gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR), and maximum payload capacity.
Comprehending your car’s weight allows you to make informed decisions about vehicle safety, performance, and fuel efficiency.
Summary
In conclusion, car weight is a critical factor that affects performance, fuel efficiency, and safety. Factors such as materials and construction, safety features, and electric vehicle batteries contribute to a vehicle’s weight. By understanding the average car weights for different body styles and the impact of weight on performance and efficiency, you can make better-informed decisions when purchasing, maintaining, and operating your vehicle. Remember to consider your car’s weight when evaluating its safety, performance, and fuel efficiency to make the best choices for your driving experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the weight of a car?
On average, a car weighs around 4,200 pounds, according to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Small cars tend to be lighter, at around 2,500 pounds, while SUVs and trucks can weigh anywhere from 3,500 pounds up to 6,000 pounds or more.
Do cars weigh 1,000 pounds?
No, cars typically do not weigh 1,000 pounds. The average compact car weighs 2,600-3,000 pounds and the average midsize car weighs 3,300 pounds, while the average large car weighs 4,400 pounds and the average subcompact SUV weighs 3,000-3,500 pounds.
How does car weight affect fuel efficiency?
Heavier vehicles require more fuel to move, leading to decreased fuel economy, while lighter cars benefit from improved fuel efficiency.
How do materials and construction methods impact a car’s weight?
The weight of a car is impacted by the materials used, such as steel, aluminum, and carbon fiber, as well as construction methods like unibody construction. This weight, in turn, affects performance, fuel efficiency, and safety.
What is the average weight of compact cars, sedans, SUVs, trucks, and sports cars?
On average, compact cars weigh 2,600 pounds, sedans 3,351 pounds, SUVs range from 3,250 to 5,700 pounds, trucks 4,000 to 7,000 pounds, and sports cars 3,100 pounds.



 Who We Are
Who We Are Coverage Area
Coverage Area Donate
Donate