If you’re wondering how long can you not move a car without causing harm, the short answer is: it depends. Parked cars may encounter issues after just a week or two of inactivity, with increased risks of damage the longer they stay put. This guide will provide you with a clear understanding of what happens when a car sits idle and how you can protect it during extended periods of non-use.
Key Takeaways
- Prolonged inactivity of vehicles can lead to issues such as flat tires, dead batteries, and rust formation which can become noticeable after two weeks and may cause severe engine damage if left for more than six months.
- Preparation for extended parking is crucial and includes stabilizing fuel, protecting the battery, and preventing rust and corrosion to avoid damage and maintain vehicle condition during inactivity.
- Regular maintenance is still necessary for parked cars, including starting the engine periodically, checking fluid levels, and tire inspection, in addition to complying with legal and insurance obligations.
The Impact of Prolonged Inactivity on Your Vehicle

Many of us believe that a car parked is a car preserved. However, vehicles are not like fine wine, which improves with age. In fact, the opposite holds true. Inactivity can lead to numerous problems, converting your valuable asset into something resembling a junk vehicle. When cars sit idle, they are prone to develop flat tires, dead batteries, and rust formation, even if they boast low mileage.
If left unattended for long periods, such as more than two weeks, these technical difficulties might manifest, and severe engine damage can occur if left for over six months. Let’s delve deeper into these issues.
Flat Tires
Regardless if it’s a car or truck, your vehicle exerts significant weight on its tires. When stationary for an extended time, the continuous pressure can lead to flat spots where the rubber meets the road. This not only results in a bumpy ride and steering difficulties but can also accelerate tire wear, requiring a potential replacement.
Sometimes, tires can lose pressure and develop warping or even tire bubbles, thereby posing a blowout risk. Therefore, it’s crucial to regularly check the pressure and integrity of tires on parked vehicles to prevent flat spots and address problems like dry rot.
Dead Batteries

Battery drain is a frequent problem in vehicles left parked for a substantial period. Even when the car is not in use, certain electronic systems continue to draw power, leading to battery drain. If a vehicle remains unused without battery maintenance, its battery could die within 4 weeks to 2 months.
Not only that, but lead sulfate can accumulate on the battery plates during prolonged storage, leading to irreversible battery damage upon complete discharge. This is indeed a big deal, and replacement parts for your vehicle might be required, increasing your costs.
Rust Formation
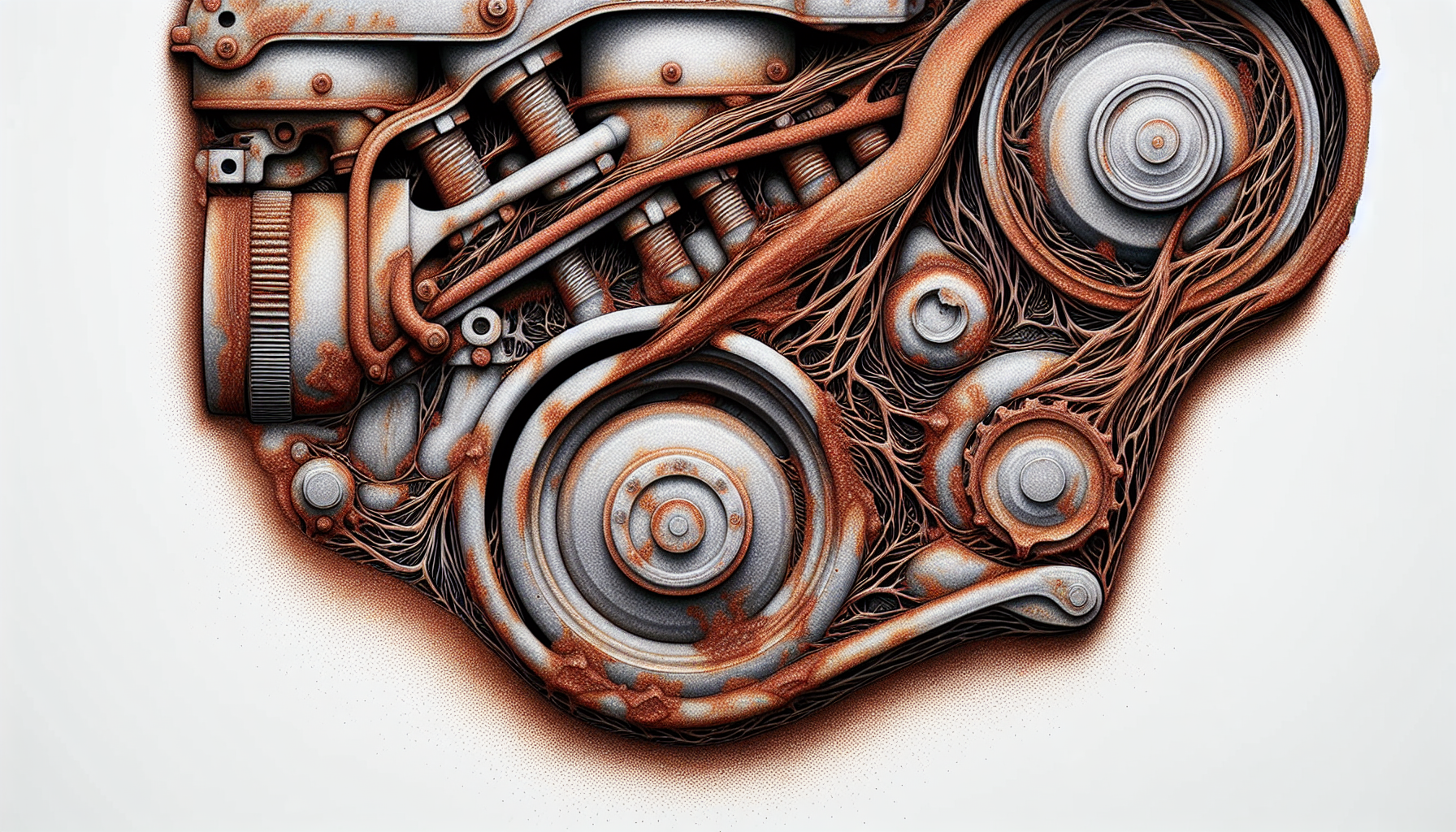
Rust formation is an additional major concern when a vehicle remains stationary for extended periods. Environmental factors such as high humidity levels and the application of road salt can expedite rusting. This rust can affect crucial parts of your vehicle, like your braking system, preventing the brake calipers from sliding correctly. The rust on brake rotors can even cause a grinding noise during the initial uses of the brakes after the vehicle has been inactive, though this noise tends to decrease after the brakes are applied multiple times.
Therefore, frequent washing of the vehicle and parking under cover can help prevent significant rust damage.
Preparing Your Car for Extended Parking
Having understood the potential risks of leaving your vehicle parked for extended periods, we’ll now discuss measures to counter these issues. It’s crucial to prepare your vehicle for extended parking. This includes stabilizing the fuel in the gas tank, protecting the battery, and preventing rust and corrosion.
It might seem like a daunting task, but don’t worry; it’s easier than it sounds. Let’s delve into these steps one by one.
Stabilizing Fuel
Stabilizing the fuel is an essential step when storing a car for extended periods. This is because gasoline can degrade over time, leading to damage to the engine. Using a fuel stabilizer can prevent this degradation.
Filling the fuel tank is also advisable to guard against moisture accumulation and safeguard engine seals. To ensure effectiveness, add the recommended amount of fuel stabilizer to a nearly empty tank, then fill the tank to between one-quarter to one-half for optimal results.
Protecting the Battery
As mentioned earlier, batteries can deplete even when the vehicle is idle. To prevent this, the battery should be removed when the car is not going to be driven for an extended period. The removed battery should be stored in a warm place to prevent the fluids from freezing and to help maintain the battery’s charge level.
This way, you can save on replacement costs and ensure your vehicle is ready to go when you need it.
Preventing Rust and Corrosion

Another essential preparation step for long-term parking is preventing rust and corrosion. This can be achieved by controlling moisture levels and providing proper ventilation in the storage space. Tools like desiccants or a CarCapsule can aid in these efforts.
Indoor, climate-controlled storage units or insulated garages offer protection from extreme temperatures and moisture, which are factors that contribute to corrosion. Keeping a car clean and promptly repairing any paint dents can also reduce the risk of rust formation.
How Long Can You Leave a Car Parked Without Driving?
Having discussed the potential issues with stationary vehicles and their prevention, you might be asking, “How long can my car remain parked without driving?” The answer to this question is not straightforward and can depend on several factors, such as the location of the parked car and how well it was prepared before being left. But with proper preparation, a car can sit without driving for months or even years.
Let’s explore these factors in more detail.
Indoor vs. Outdoor Storage
The condition of your vehicle over time can be significantly affected by its storage location. Indoor storage in a garage or public storage facility provides the best protection from weather and helps maintain a stable temperature. However, this option is typically more expensive and may have limited availability.
On the other hand, outdoor storage is a more affordable option and can accommodate larger or multiple vehicles but increases the car’s exposure to the elements and may offer less security.
Climate Factors
The climate where your vehicle is parked significantly influences how long it can remain stationary without driving. Here are some effects of different climates on your vehicle:
- Extreme cold can cause engine oil and other fluids to thicken, which may prevent the engine from starting and lead to the need for costly repairs.
- Hot temperatures can accelerate the deterioration of vehicle components.
- High humidity environments can accelerate rust formation.
Therefore, it’s essential to consider climate factors when deciding where and for how long to park your vehicle.
Vehicle Type and Age
Lastly, your vehicle’s type and age can also affect the duration it can stay parked. Newer cars with more advanced electronics and battery management systems might be less prone to battery drain when not driven for some time. However, older vehicles with fewer electronic components may not face the same level of risk for certain types of degradation.
Aged vehicles could have seals and gaskets that are more prone to dry out and crack if the car is not driven regularly. Therefore, it’s essential to take into account the specific characteristics of your vehicle when planning for extended parking.
Regular Maintenance for Parked Cars
Despite preparing your vehicle for long-term parking, regular maintenance is vital to keep it in good condition. While your car is parked, you should start the engine periodically, check fluid levels, and inspect the tires.
Let’s delve into these maintenance tasks in more detail.
Starting the Engine

Regularly starting the engine is a straightforward way to maintain your parked vehicle. This helps the fluids to circulate properly and maintain the battery’s charge. It’s recommended to start the engine every week and let it run for at least 15 minutes.
If possible, drive the car for at least 20 minutes every two weeks to prevent issues like a stale fuel system or a drained battery.
Checking Fluid Levels
Another essential maintenance task is to check and adjust your vehicle’s fluid levels. Be sure to check the levels of essential fluids such as:
- oil
- brake fluid
- transmission fluid
- power steering fluid
- differential fluid
These fluids can deteriorate over time, so it’s important to regularly check and maintain them.
It’s also important to inspect both engine and cabin air filters for contaminants. Remember, avoiding overfilling fluid levels is as essential as running with too little fluid.
Inspecting Tires
Finally, remember to inspect the tires of your stationary vehicle. Tires can lose air over time, leading to underinflation or even flat tires if the car is not moved for an extended period. Therefore, it’s crucial to check and adjust their pressures regularly to ensure they are within the recommended levels for safe vehicle operation.
Legal and Insurance Considerations for Parked Vehicles
Alongside addressing your vehicle’s physical needs during prolonged parking, legal and insurance considerations are equally important. Local ordinances regulate the conditions under which a vehicle can be parked, and property owners have specific responsibilities concerning the storage of vehicles. Additionally, proper auto insurance coverage is vital even when a car is not in use.
Let’s delve into these considerations.
Local Ordinances
Local ordinances usually have unique definitions and regulations for stopping, standing, and parking. Knowing these definitions is crucial to comply and avoid parking violations.
For example, in most states, cars that are parked on public roads must carry at least the state’s minimum liability insurance coverage, even if they are not being actively driven. So, it’s always a good idea to be aware of the regulations in your area to avoid any legal complications.
Property Owner Responsibilities
Being a property owner, you bear particular responsibilities regarding your vehicle. Even if it’s parked on your property, you must ensure it has insurance coverage. Damages incurred from incidents like hit-and-runs on private property will not be covered without it.
Thus, always ensure you have valid insurance coverage for your parked vehicle.
Auto Insurance Coverage
Maintaining appropriate auto insurance coverage is crucial for stationary vehicles, whether driven actively or not. Owners of vehicles that are still being financed are generally required to carry full insurance coverage to protect the lender’s investment. However, car insurance can’t be paused or suspended at will. You can reduce your coverage to the minimum or opt for storage insurance, which includes only comprehensive coverage and is cheaper than regular insurance.
Keep in mind that insurance for a parked car may require the vehicle to be in storage for at least 30 days.
Dealing with Vehicle Recalls and Repairs During Extended Parking
What happens if your vehicle requires repairs or is recalled during its extended parking period? Dealing with these issues requires some planning and proactive steps. It’s essential to stay informed about potential recalls and repair needs for your vehicle, even when it’s not in use.
In this section, we’ll explore how to identify recalls, schedule repairs, and consider rental car options during extended parking.
Identifying Recalls
If your vehicle faces a recall, immediately notifying the manufacturer or dealer is critical to ensure problem resolution once the car is back in use. Car owners affected by a recall may request a loaner vehicle from their dealer while waiting for the repair.
This way, you can ensure your vehicle is safe and ready to drive when you need it, all in the same place.
Scheduling Repairs
Should your vehicle need repairs while parked for a long duration, advance contact with a trusted mechanic or dealership is vital. Consider their policies on customer presence and the payment structure for their mechanics. This way, you can ensure your vehicle is in good hands and will be ready for use when needed.
Rental Car Options
During recall repairs, dealerships may provide loaner vehicles to affected owners, with manufacturers authorizing payments for these loaners. Guaranteed replacement coverage is an insurance option that may replace a car if it is less than three years old, offering certainty during long repair periods.
This way, you can ensure you have a mode of transportation while your vehicle is being repaired, without the need for a temporary car sit.
Reviving Your Car After a Long Period of Inactivity
When you’re set to start using your vehicle post a lengthy period of inactivity, there are crucial steps to follow to ensure the car is safe and road-ready. First, you’ll need to check the fluids, inspect the vehicle, and warm up the engine. This will ensure your car is in top shape and ready to handle any trip you have planned.
Let’s discuss these steps in more detail.
Checking Fluids
After a vehicle has been idle for a long period, it’s important to check and evaluate the levels and quality of key fluids like:
- oil
- brake fluid
- transmission fluid
- power steering fluid
- differential fluid
These fluids can degrade over time. It’s also important to inspect both engine and cabin air filters for contaminants.
Remember, avoiding overfilling fluid levels is as essential as running with too little fluid.
Inspecting the Vehicle
A comprehensive vehicle inspection after prolonged inactivity should include:
- Checking the brakes for rust
- Assessing the charging and starting system, including the battery and alternator
- Ensuring oil quality is adequate
- Inspecting both engine and cabin air filters for contaminants
- Evaluating tires for dry rot and proper inflation
These steps are important to ensure that your vehicle is in good condition after a period of inactivity.
A thorough visual inspection of a car should include checking for signs of animal nesting or infestation and assessing the condition of belts, hoses, and wires for any damage or deterioration.
Warming Up the Engine
Letting the engine idle for a few minutes post-startup aids in proper fluid circulation and achieving optimal operating temperature. This is especially important in cold weather, where it’s recommended to let the car engine run for about one minute to ensure proper lubrication of engine components.
Rather than simply idling, it is advisable to drive the car for at least 10-15 miles at speeds above 50 mph to maintain the engine in good condition.
Summary
We’ve covered a lot of ground in this post, from the potential damage caused by prolonged vehicle inactivity to the steps to prepare your car for extended parking, regular maintenance, and legal and insurance considerations. We also touched on how to handle vehicle recalls and repairs during extended parking and how to revive your car after a long period of inactivity. Remember, a little preparation and regular attention can go a long way in keeping your vehicle in good shape, even when parked for extended periods.
Frequently Asked Questions
What problems can occur if a car is left parked for a long time?
Leaving a car parked for a long time can lead to flat tires, dead batteries, and rust formation, which may result in severe engine damage if the car is left unattended for over six months.
How can I prepare my car for extended parking?
To prepare your car for extended parking, stabilize the fuel, protect the battery, and prevent rust and corrosion. This will help to ensure your car remains in good condition during its time of inactivity.
How often should I start my parked car?
It’s best to start your parked car every week and let it run for at least 15 minutes, and if you can, take it for a 20-minute drive every two weeks. This helps maintain the health of your car’s engine and battery.
Do I need to maintain insurance on a parked car?
Yes, you need to maintain proper auto insurance coverage for parked vehicles, even if they are not actively driven. It’s important to ensure your car is protected at all times.
How do I revive my car after a long period of inactivity?
To revive your car after a long period of inactivity, you should check fluids, inspect the vehicle, and warm up the engine. These steps will help ensure your car is in good working condition.
For more information, visit https://www.carmula.com/



 Who We Are
Who We Are Coverage Area
Coverage Area Donate
Donate